Extracting Discriminative Features using Task-oriented Gaze Maps Measured from Observers for Personal Attribute Classification
[Abstract]
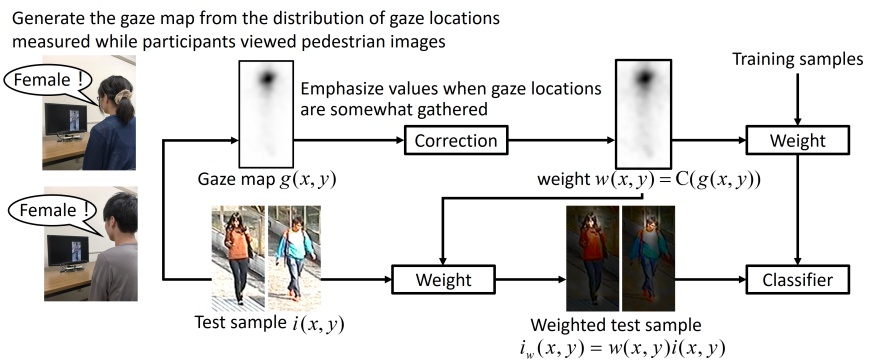
We discuss how to reveal and use the gaze locations of observers who view pedestrian images for personal attribute classification. Observers look at informative regions when attempting to classify the attributes of pedestrians in images. Thus, we hypothesize that the regions in which observers' gaze locations are clustered will contain discriminative features for the classifiers of personal attributes. Our method acquires the distribution of gaze locations from several observers while they perform the task of manually classifying each personal attribute. We term this distribution a task-oriented gaze map. To extract discriminative features, we assign large weights to the region with a cluster of gaze locations in the task-oriented gaze map. In our experiments, observers mainly looked at different regions of body parts when classifying each personal attribute. Furthermore, our experiments show that the gaze-based feature extraction method significantly improved the performance of personal attribute classification when combined with a convolutional neural network or metric learning technique.
[Publications]
- Michiko Inoue, Masashi Nishiyama, and Yoshio Iwai,
Age Group Identification Using Gaze-Guided Feature Extraction,
Proceedings of IEEE 12th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), POS, pp. 711 - 714, October 2023.
[Poster]- Masashi Nishiyama, Riku Matsumoto, Hiroki Yoshimura, Yoshio Iwai,
Extracting Discriminative Features using Task-oriented Gaze Maps Measured from Observers for Personal Attribute Classification,
Pattern Recognition Letters (PRL), vol. 112, pp.241 - 248, September 2018.- Riku Matsumoto, Hiroki Yoshimura, Masashi Nishiyama, Yoshio Iwai,
Feature Extraction using Gaze of Participants for Classifying Gender of Pedestrians in Images,
Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3545 - 3549, September 2017.